P615
Cushing’s syndrome results in abnormally high levels of cortisol in the bloodstream for extended periods of time. Cortisol production is regulated by the hypothalamic pituitary adrenal (HPA) axis set of endocrine glands. The feedback mechanism for the pathway is shown in Figure 1.
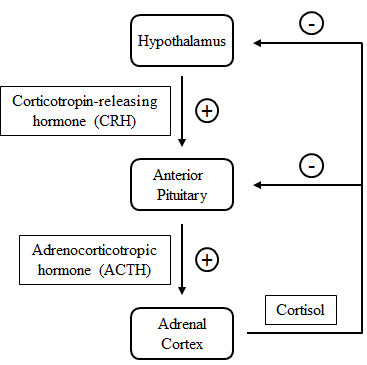
Figure 1. Signaling pathway leading to the production of cortisol.
A study examining the effects of various drugs on the HPA axis was conducted in which mice were injected with a variety of hormones. 4 groups of mice were injected with various chemicals. Group 1 was injected with cortisol, Group 2 was injected with angiotensin (a hypothalamus stimulant), Group 3 was injected with saline solution, and Group 4 was injected with a laboratory generated hormone X. The blood concentration of various hormones in the mice was measured, and the results are presented in Table 1 below.
Table 1. Concentrations of HPA hormones in different test groups (nmol/L).
In order to treat Cushing’s, two approaches can be taken. The HPA pathway can be targeted in order to downregulate production of cortisol, or the cortisol synthesis pathway, seen below, can be targeted.
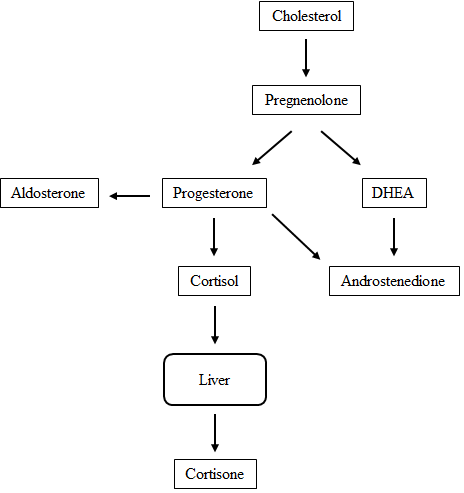
Figure 2. Metabolic pathway for production of cortisone from cholesterol.
.
Find an error? Take a screenshot, email it to us at error@mytestingsolution.com, and we’ll send you $3!
