P423
Cyclodextrins (CDs) are an important class of biological molecules widely investigated for their solubility-enhancing properties. CDs are composed of glucopyranose subunits attached by &alpha-(1,4) linkages and assembled into a ring shape. Various types of CDs exist, varying largely by the number of glucopyranose units. These oligosaccharides have hydrophilic exteriors while maintaining relatively hydrophobic interiors.
In one study, researchers investigated modified CDs for their enhanced solubility and drug-carrying capacity. Researchers complexed sulfobutyl ether β-cyclodextrin (SBE-β-CD) with erlotinib hydrochloride (ERL), a tyrosine kinase inhibitor specific to the epidermal growth-factor receptor. ERL has been investigated for its anti-cancer properties. However, its poor solubility limits its bioavailability.
.
Figure 1. Structure of erlotinib.
.
A 1:1.05 molar ratio of ERL:SBE-β-CD was investigated for its pharmacokinetic properties and compared with ERL alone.
.
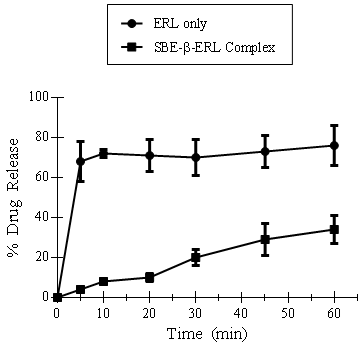
Figure 2. Drug release over time using SBE-β-CD complexed with ERL, and ERL only.
.
The ERL-SBE-β-CD complex was characterized by infrared (IR) spectroscopy. the frequency of vibration for any given bond can be estimated using Equation 1 where k is the spring constant and μ is the equivalent mass of the functional group.
.
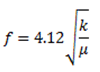
Equation 1
.
Find an error? Take a screenshot, email it to us at error@mytestingsolution.com, and we’ll send you $3!
