P403
Ferric thiocyanate is a brick-red complex ion that is stable in an aqueous environment. In water, the ferric ion exists as a hydrated octahedral complex, Fe(H2O)63+. In the presence of thiocyanate ion (SCN–), the ferric thiocyanate ion is produced.
Fe3+(aq) + SCN–(aq) ↔ Fe(SCN)2+(aq)
Reaction 1
Since this product increases the concentration of protons present when added to water, it possesses Arrhenius acidic character. To determine the equilibrium constant for Reaction 1, various ratios of Fe3+ and SCN– are combined and absorbance is measured with a spectrophotometer over ten trials.
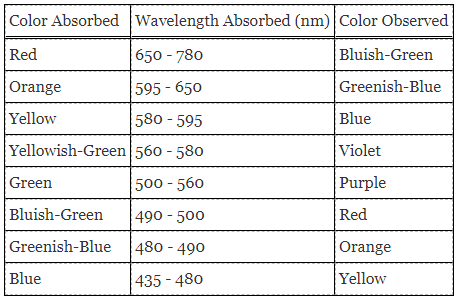
The absorbance for the first five trials is measured and plotted against the known concentration of the FeSCN2+ (or initial SCN–) in order to help determine the concentration of FeSCN2+ for next five trials. The spectrophotometer is set to a wavelength consistent with the maximal absorbance of the compound.
.
Find an error? Take a screenshot, email it to us at error@mytestingsolution.com, and we’ll send you $3!
