P818
Social capital refers to the networks of relationships that exist among individuals in a society as well as the relationships that generate long-term individual and collective benefits. Social capital enables the sharing of information and social norms and generates confidence that others will conform to these norms. It has therefore been seen as a solution to collective action problems, which exist when the benefits of cooperating exceed the costs of cooperating, but a lack of trust and individual incentives inhibits the cooperation. Although there is some disagreement among researchers about causes and consequences of social capital, measures of social capital are positively correlated with a variety of positive social outcomes.
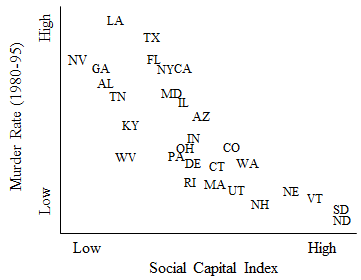
Figure 1. State-level social capital and murder rates.
A major study of social capital published in 2000 documented the decline of social capital in the United States and the consequences of this decline. The study created a single index of social capital for each state by combining a variety of measures of social connections, cooperation, and trust in a given state, such as data on voter participation, rates of volunteering, and trust in others as reported in a survey. Figure 1 shows a graph of states’ social capital and their murder rates over the period from 1980 to 1995, with each state represented by its two-letter abbreviation.
.
Find an error? Take a screenshot, email it to us at error@mytestingsolution.com, and we’ll send you $3!
