P406
The borax buffering system is crucial to the study of biochemistry and is often used in histology. The titration of hydrochloric acid to a concentrated solution of a base such as borax reveals the thermodynamic values of enthalpy (ΔH), entropy (ΔS), and Gibbs free energy (ΔG) as a function of temperature. Borax, composed of sodium and tetraborate ions, is separated into three ions via an endothermic reaction. The ions are then hydrated in an exothermic reaction. They hydration results in the ions being surrounded by water through polar attraction.
Equation 1
The amount of acid required to neutralize the tetraborate ion in solution facilitates determination of the amount that dissociated, which will vary with temperature. Performing this experiment at different specified temperatures enables the state functions to be calculated using Ksp as a function of temperature.
At equivalence, the reaction B4O5(OH)42- (aq) + 2H+ (aq) + 3H2O (l) → 4H3BO3 (aq) will have occurred, reaching its endpoint. The addition of the blue-to-yellow indicator makes the equivalence point of this reaction more apparent, so that the amount of titrant added can be measured and the thermodynamics properties of the reaction determined.
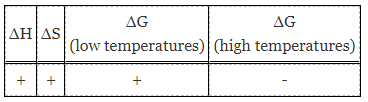
Table 1. Thermodynamic Data for Equation 1.
.
Find an error? Take a screenshot, email it to us at error@mytestingsolution.com, and we’ll send you $3!
