P643
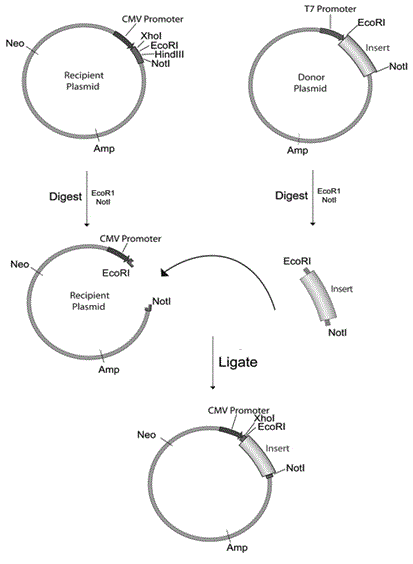
“Figure 1 below gives a standard subcloning for transferring a DNA fragment (insert) from the donor to the recipient plasmid. It involves three steps:
1. Releasing the insert from the donor plasmid and its purification
2. Digestion of the recipient plasmid
3. Ligation of the insert into the recipient ligations.
The release of insert is accomplished using restriction enzymes that recognize specific sequence of DNA and cleave the phosphate backbone of the DNA molecule near that sequence. Once digestion of the DNA fragments is carried out with enzymes that generate compatible ends ligation is carried out using DNA ligases.
Amp and Neo indicated on the plasmids in the figure are antibiotic markers that confer resistance to ampicillin and neomycin respectively. The ligated plasmids are transformed into bacteria which are selected using appropriate antibiotics, depending on the antibiotics markers on the plasmids. The restriction digestion sites shown in the figure are part of multiple cloning site, and are present only as a single copy to facilitate ease of cloning. Among these enzymes, the ones that do not cleave the insert fragment (so that it can be released intact) are used for cloning.
.
Find an error? Take a screenshot, email it to us at error@mytestingsolution.com, and we’ll send you $3!
