P623
Atherosclerosis is a chronic inflammatory disease that manifests in the walls of blood vessels by the accumulation of white blood cells, fat, cholesterol, calcium, and other substances found in the blood. These accumulations are referred to as plaque. It has been established that both the antibody and cell-mediated components of the immune system are present in this disease. Kawasaki Disease is a multisystem inflammatory disease with unknown etiology. It is a leading cause of non-congenital heart disease among children.
The following study was performed to investigate the possibility that Lactobacillus casei cell wall extract (LCWE)-induced Kawasaki Disease quickens atherosclerosis in hypercholesterolemic mice. An experiment was designed in which mice lacking apoliprotein E (Apoe-/-) were injected with LCWE and fed a high fat diet for 8 weeks. These mice were compared to Apoe-/- mice that received a phosphate buffer saline (PBS) solution instead of the LCWE. Study evaluation involved measuring the presence of atherosclerotic lesions in multiple regions of the aorta. To elucidate the details of immune system involvement in disease progression, serum concentration levels of multiple pro-inflammatory cytokines such as a tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-&alpha), interferon gamma (IFN-γ), and interleukins such as IL-12p40 were measured in the mice.
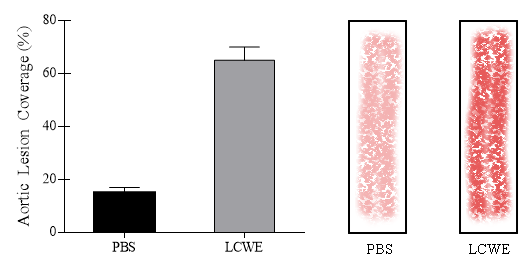
Figure 1. Aorta lesion coverage and representative Oil Red O staining from Apoe-/- KD and Apoe-/- non-KD mice.
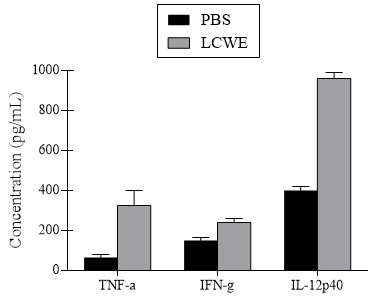
Figure 2. Serum concentrations of TNF-α, IFN-γ, and IL-12p40 obtained at the end of the high fat diet.
.
Find an error? Take a screenshot, email it to us at error@mytestingsolution.com, and we’ll send you $3!
