P606
Aldosterone is a hormone produced by the adrenal cortex and its release into the bloodstream plays a major role in the regulation of blood pressure. The homeostatic control of blood pressure is dependent primarily on the adrenal cortex, liver, and kidneys, as shown in the figure below.
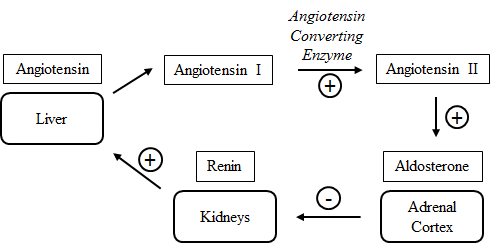
Figure 1. Aldosterone regulatory pathway.
In the kidneys, low blood volume signals the juxtaglomerular cells in kidney nephrons to produce renin, which upregulates the conversion of angiotensin into angiotensin I. Later, angiotensin converting enzyme converts angiotensin I to angiotensin II, which directly stimulates the adrenal cortex to produce aldosterone. Angiotensin has several physiological functions by itself, including increasing vasoconstriction of arteries and increasing the rate of reabsorption of sodium into nerve cells.
Recent work has generated four new drugs which are believed to be capable of reducing blood pressure and treating hypertension. The drugs were tested on 100 subjects that were selected based on chronically high blood pressure of over 160/110. The subjects were divided into four groups of 25 patients each and given a daily dose of their assigned drug in 15 mg pills.
Table 1. Results of drug study on blood pressure, urine volume, and urine sodium concentration.
| Treatment | Blood Pressure Average |
Urine Volume (L/day) |
Urine Sodium Concentration (mg/L) |
| Drug 1 | 120/105 | 2.55 | 185 |
| Drug 2 | 118/76 | 1.75 | 53 |
| Drug 3 | 147/98 | 2.45 | 40 |
| Drug 4 | 122/75 | 1.2 | 145 |
| Control (low blood pressure) |
117/87 | 1.75 | 57 |
.
Find an error? Take a screenshot, email it to us at error@mytestingsolution.com, and we’ll send you $3!
