P421
Cystic fibrosis is a genetic disorder that can affect the lungs, liver, kidneys, and intestines. Younger patients with cystic fibrosis are at a high risk of developing pulmonary infections, such as those caused by caused Pseudomonas aeruginosa bacteria. This bacteria secretes a substance known as alginate, a polysaccharide capable of absorbing large amounts of water and forming mucus. This mucus also contains lipopolysaccharides (LPS), which contribute to the severity of the pulmonary infection.
.
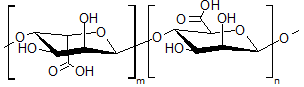
Figure 1. Molecular structure of alginate.
.
Alginate is formed by the enzyme phosphomannomutase (PMM), which converts mannose-1-phosphate (M1P) into the alginate base structure. LPS is formed by phosphoglucomutase (PGM), which uses glucose-1-phosphate (G1P) as a starting molecule. P. aeruginosa contains a bifunctional enzyme known as PMM/PGM, which displays a high activity of both enzymes. Researchers conducted experiments in order to assess the characteristics and reaction rate of this enzyme.
In the first experiment, a cell extract of P. aeruginosa was extracted and tested for the presence of PMM/PGM by assessing its reactivity with mannose-1-phosphate and glucose-1-phosphate.
In the second experiment, the cell extract was run through a series of gel column filtrations, and after each filtration, the extract was run on an SDS-PAGE gel.
.
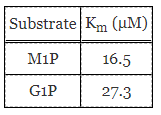
Table 1. Experiment 1 results of PMM/PGM activity with M1P and G1P substrates.
.
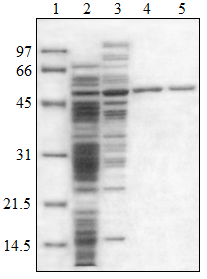
Figure 2. SDS-PAGE of cell extract purification. Lane 1 = ladder, Lane 2 = cell extract, and Lanes 3-5 = subsequent purifications of the PMM/PGM enzyme. Ladder is in kDa.
.
The third experiment tested the hypothesis that magnesium is an essential ion required for the function of PMM/PGM. The concentration of the the M1P and G1P substrates were plotted over time with and without magnesium present for the enzyme.
.
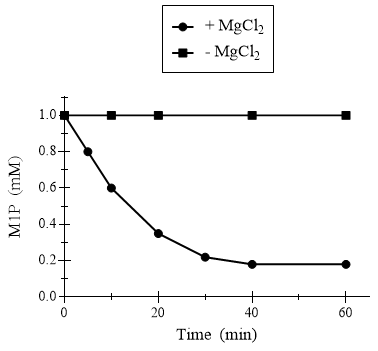
Figure 3. Effect of magnesium on PMM/PGM activity with M1P substrate.
.
.
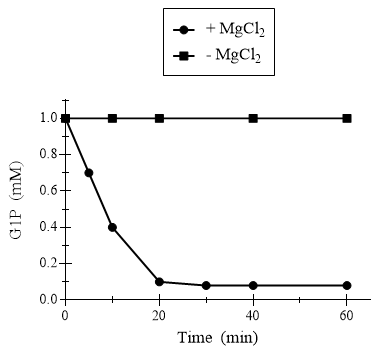
Figure 4. Effect of magnesium on PMM/PGM activity with G1P substrate.
.
Find an error? Take a screenshot, email it to us at error@mytestingsolution.com, and we’ll send you $3!
