P1033
Flavoproteins are proteins that contain a nucleic acid derivative of riboflavin; such examples include FAD or FMN. Flavoproteins are involved in a wide array of biological processes, including removal of reactive radicals contributing to oxidative stress, DNA repair, and apoptosis. Epidermin is a crucial protein in the oxidative phosphorylation pathway important to sequester oxidative species while transferring electrons via a flavoprotein FMN to different complexes in the transport chain as seen in Figure 1. FMNH2 donates the electrons it receives and is thus consumed in the electron transport chain.
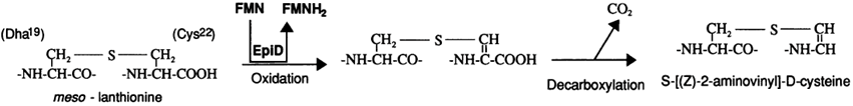 Figure 1. Epidermin pathway, labeled EpiD
Figure 1. Epidermin pathway, labeled EpiD
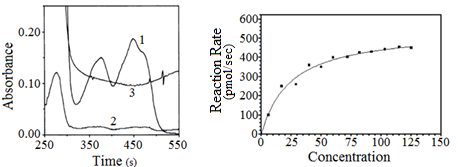 Figure 2. Pyruvate dehydrogenase kinetics and absorbance
Figure 2. Pyruvate dehydrogenase kinetics and absorbance
Different absorbencies were recorded of the byproducts formed by the reaction in Figure 1 as well as the enzyme kinetics of the important enzyme pyruvate dehydrogenase in the oxidative phosphorylation pathway. These graphs depict the overall progress of the reaction scheme of Figure 1 and can be manipulated using different drugs that inhibit various complexes in the mitochondrial membrane.
Find an error? Take a screenshot, email it to us at error@mytestingsolution.com, and we’ll send you $3!
